Organizations today view their data assets as key business drivers for competitive advantage. However, the cost of running analytic solutions is drastically increasing while speed-to-deployment remains a major challenge. Businesses know that they have vast amounts of data assets available across a strata of resources, but can have difficulty drawing any meaningful insights from these resources.
Enterprises everywhere are seeking a comprehensive data analytics solution to help reduce costs, speed up development cycles and deliver valuable insights solving some of their largest organizational problems.

Veracity, Velocity, Variety and Volume
As it stands now, most enterprise data is stored in a data lake, which contains all the available data (variety, volume) in a centralized, commodity storage. One pitfall of relying on information contained in a data lake is that the high volume of information from a variety of sources makes it difficult to know where it is and where it came from and what it means. In other words it is difficult for data consumers to understand the context of the data. In turn, this makes it difficult to trust its veracity as well as put it to good use.
Democratizing big data management through Hadoop and a semantic layer
Hadoop and a semantic layer both address several problems with sourcing from a data lake, including the:
- Velocity – how fast the data comes into the data lake
- Variety – Hadoop allows you to store the data from both structure and unstructured sources
- Volume – how much data you can store
- Veracity – how reliable and understandable your data resources are
This is where a semantic layer can be applied to address the problems of variety and veracity. A semantic layer acts like a business-user understandable roadmap that gives everyone directions and context while providing key business meaning needed to achieve insights from your data assets. Semantic layer technologies can easily integrate data through simplified and sophisticated modeling processes that both connects information from multiple sources and provides its business meaning free from artifacts of how it was formatted or stored for example obscure table and column names or short-hand application specific codes for data value elements.
The semantic layer is easily accessible to all users across the organization and they can use it to far more quickly extract the answer to their particular use case. A semantic layer maps complex data into familiar business terms such as product, customer, or revenue to offer a unified, consolidated view of data across the organization. By mapping your data sources into a highly normalized business model (aka semantic layer), analysts and business stakeholders are provided with a common lingua franca and understanding across teams and business units although the technology also allows them to maintain a private understanding of it too if they wish – there is no need for a “single version of the truth” as a semantic model can also provide different “lenses of understanding” for different groups whenever needed.
The Hadoop software family is a popular open-source suite of programs that allow IT groups and data scientists alike to form the ‘backbone’ of their data analytics operations. Hadoop serves as an extremely helpful tool that, when combined with a semantic layer technology, can solve the fundamental issue in which you don’t need to go through several people and long iterative processes to manipulate data into the form that you need to answer a question as all the data stored, connected, described and queried in one convenient location.
Along with Hadoop, businesses can leverage platforms that provide a semantic layer to quickly achieve insights for faster and more informed decision-making. With a rich and interactive semantic layer, data and analytics stacks deliver true on-demand access to data, answers, and insights, weaving data together from across the enterprise into an information fabric.
The Solution – Anzo®
Cambridge Semantics’ Anzo 4.0 offers a coding-free, end-to-end, enterprise-scale open platform that creates a single semantic layer of an organization’s structured and unstructured data. The resulting product is a business-friendly, fully governed data fabric that is capable of managing all enterprise data, while also enabling users to conduct code-free, rich interactive discovery and analytics at speeds more than 100x faster than competing approaches.
With Cambridge Semantics’ open standards approach and the semantic layer provided by Anzo 4.0, enterprises have both a venue and a means of translation of all enterprise data so that it is meaningful and understandable to the language of the end user, department or organization. The connected data is so well-described at a business level that it can quickly be combined and reused in any manner. This allows enterprises to become far more agile with quick iterations and fast pivots to evolve and tackle follow-on or new questions immediately.
Anzo uses a W3C open data standard (RDF and OWL) to represent its models.
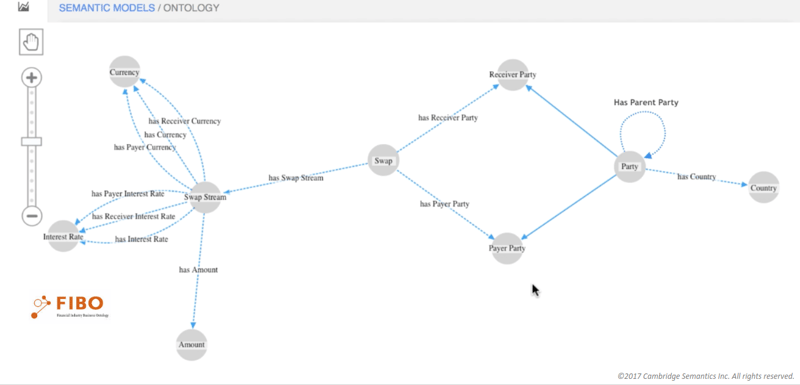
Enterprises can address the data veracity challenges and allow analysts to find relevant data more rapidly by investing in a data foundation that gives meaning to a data lake through a semantic layer. The semantic layer also provides a business-friendly mapping tool which auto-generates Spark jobs and a self-service data feed optimized for consumption. This enables people across an organization to iterate and experiment with their use case while keeping governance and compliance in check.
Learn more about creating a Semantic Layer for Hadoop using Anzo.

