We are at an inflection point in the financial services industry. The evolving and overwhelming demands of regulatory compliance have forced organizations to acknowledge the need for data governance and most are developing their strategy.
 Implementing true enterprise wide data governance faces many obstacles. Most organizations are dealing with applications and data sources implemented over decades in a myriad of formats and technologies. Manual data quality processes are the weak link in financial data management with many organizations are still throwing people and spreadsheets at the problem.
Implementing true enterprise wide data governance faces many obstacles. Most organizations are dealing with applications and data sources implemented over decades in a myriad of formats and technologies. Manual data quality processes are the weak link in financial data management with many organizations are still throwing people and spreadsheets at the problem.
Justifying the capital investment to harmonize data across these sources is challenging and many organizations are forced to get by with expensive, labor intensive “spreadsheet enabled” processes. This error prone and expensive approach is not sustainable as labor costs increase and fines escalate.
The good news is that Data Governance does not have to be a tax on the business. In fact, smart organizations recognize it as an opportunity to create a powerful data ecosystem that can be a valuable asset to the organization beyond regulatory reporting by supporting business transformation and driving new revenue. Harmonized, high-quality, well-governed data is not just for regulatory compliance – it is an essential enabler for competitive differentiation.
Cambridge Semantics has developed an approach to data governance based on the Smart Data Lake® solution to harness this opportunity.
Business Drivers
BCBS 239 is one of the key drivers for data governance initiatives, especially in Tier 1 institutions, and it is can be described in four key categories:
- Overarching Governance and Infrastructure
- Risk Data Aggregation
- Risk Reporting Practices
- Supervisory Review, Tools and Cooperation
To comply with the BCBS 239 principles requires an unprecedented level of data governance and operational activities including:
- Robust data management and governance and repeatable business processes with auditability and impact analysis
- Well described, high-quality, timely, accurate, complete and traceable data; Harmonized based on its meaning
- Reporting and analytics across diverse sets of internal and external data for different target audiences
- Adaptability to changing business processes, organizations, systems, and reporting requirements
- Security

Read also: FIBO, FIBO, It's Off to Work We Go ![]()
Solution: The Smart Data Lake
Retroactively applying these requirements to an existing infrastructure is a monumental task. Fortunately, there is an emerging approach which allows an organization to meet the regulatory requirements, provide a foundation for a robust and valuable data ecosystem, all while leaving existing processes and infrastructure in place. That is the Smart Data Lake.
The Data Lake is a modern approach to enterprise data architecture that provides a great way to rapidly and inexpensively assemble large volumes of unfiltered data for management and analytics. Leveraging cheap storage and commodity hardware, the data lake offers an unprecedented opportunity to democratize access to enterprise data. However, the data lake comes with its own challenges:
- How to catalog, identify and link data in the lake?
- How to harmonize meaning across diverse sources and making it accessible to business users?
- How to deliver good data governance, quality, lineage and security?
Leading organizations are turning to semantic models and tools to address these challenges, hence the Smart Data Lake.
There are several main advantages to Smart Data Lake approach:
1. Industry Standards Based Data Harmonization
 Semantic models provide a common business vocabulary and meaning across diverse data sources, structured and unstructured. This enables harmonization of data from disparate sources through common business meaning. Emerging data model standards such as the Financial Industry Business Ontology (FIBO) from the EDM Council offer a way to harmonize data and meaning across the entire industry for participants and regulators.
Semantic models provide a common business vocabulary and meaning across diverse data sources, structured and unstructured. This enables harmonization of data from disparate sources through common business meaning. Emerging data model standards such as the Financial Industry Business Ontology (FIBO) from the EDM Council offer a way to harmonize data and meaning across the entire industry for participants and regulators.
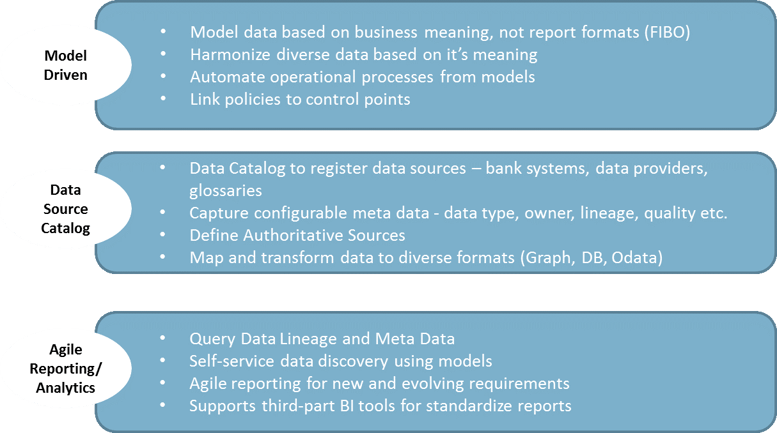
2. Model Driven
 Model driven data governance and transformation automates the link between governance and data. It enables active meta data management for data lineage, impact analysis, meta-data analytics, meaning, data, transformation, and usage. By generating executable processes from the models we use to govern and harmonize data, we ensure they are always in sync and up to date. Since we can also query these models, we make this information easily accessible to a broad business community.
Model driven data governance and transformation automates the link between governance and data. It enables active meta data management for data lineage, impact analysis, meta-data analytics, meaning, data, transformation, and usage. By generating executable processes from the models we use to govern and harmonize data, we ensure they are always in sync and up to date. Since we can also query these models, we make this information easily accessible to a broad business community.
3. Tools
 Model driven tools built on the semantic standards put data cataloging, harmonization, discovery, lineage and analytics in the hands of business analysts. These tools are also agile, flexible and adaptable to new requirements so easily accommodate the evolcing regulatory needs and the growing demands from the business.
Model driven tools built on the semantic standards put data cataloging, harmonization, discovery, lineage and analytics in the hands of business analysts. These tools are also agile, flexible and adaptable to new requirements so easily accommodate the evolcing regulatory needs and the growing demands from the business.
4. Data Re-use
A critical advantage of the Smart Data Lake is data re-use. By harmonizing your data across diverse sources and describing it in business terms, you can it easily make it available for diverse use cases beyond regulatory reporting. Self-service tools allow business users to select, combine and query any data set in the lake (based on entitlement). This opens up the data for customer, revenue, fraud and other use cases.
Smart Data Lake Characteristics
Conclusion
Regulatory reporting requirements are driving the adoption of data governance. Smart institutions recognize this as an opportunity to leverage emerging capabilities like the Smart Data Lake to create a data ecosystem that can not only satisfy the regulatory reporting needs but also create a data platform that differentiate them in the market.
To learn more, watch our webinar "Applying Data Engineering and Semantic Standards to Tame the 'Perfect Storm' of Data Management".

